This information should always be used alongside other performance metrics to provide an accurate picture for investors. Accrued revenue and expenses can be manipulated, which means that net income may not always accurately represent how profitable a business is. Accruals also make it more difficult to track both current and past performance metrics because investors will have to rely on estimates until these transactions actually occur for real. Accruals provide information that will allow investors to track performance more accurately than they would otherwise be able. Accrual accounting remains an integral part of financial accounting today because it allows businesses to account for all transactions that have yet to take place concerning revenues and expenses alike. Accrual accounting differs from cash accounting because it includes revenue that has yet to be collected (accounts receivable) and expenses that have yet to be paid out (accounts payable).
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
The IRS’s guide to accrual and cash accounting can help you understand the basics, but working with an accountant to file your business taxes is the best way to minimize confusion about income tax payments. Accrued revenue occurs when a company has delivered a good or provided a service but hasn’t yet received payment. These accounts are often seen in the cases of long-term projects, milestones, and loans. When a company receives cash before a good has been delivered or a service has been provided, it creates an account called deferred revenue, also referred to as unearned revenue. This account is a liability because the company has an obligation to deliver the good or provide the service in the future.
Bank Reconciliation Made Easy: A Step-by-Step Guide to Achieving Financial Accuracy
- For example, let’s say a customer paid $100 for your consulting services in January, but you’ll only be providing the service in February.
- By doing so, they help align the financial records with the actual economic activities of the business, providing a more accurate picture of its financial health.
- Transitioning to and maintaining an accrual accounting system can incur higher costs.
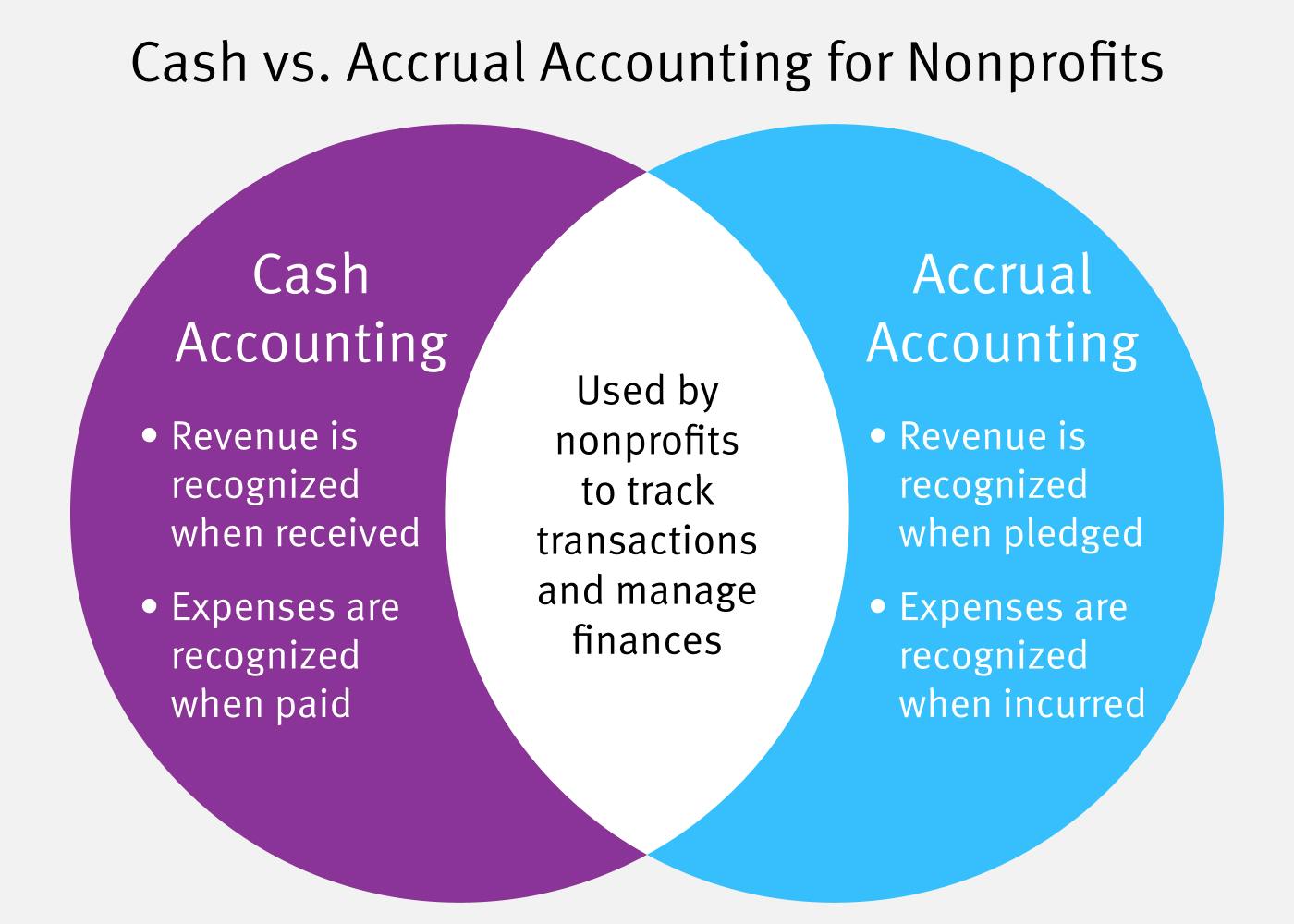
- Small businesses and individuals may find the cash basis method more suitable, while larger businesses and corporations may prefer the accrual method for a more accurate financial picture.
- Alternatively, if the campaign’s impact canot be directly linked to future sales, the entire expense might be recognized in December.
One of the key benefits of accrual accounting is that it allows companies to match revenue and expenses more accurately. For example, if a company sells a product in December but does not receive payment until January, the revenue is still recognized in December because that is when the sale was made. This helps to ensure that the company’s financial statements accurately reflect its performance during the period bookkeeping training certificate in question. Accrual accounting is an accounting method in which payments and expenses are credited and debited when earned or incurred. Accrual accounting differs from cash basis accounting, where expenses are recorded when payment is made and revenues are recorded when cash is received. While accrual accounting is the most widely used accounting method, some businesses prefer to use cash basis accounting.
Principles of Accrual Accounting
In this post, we’ll go over what you need to know about the accrual method of accounting, including its benefits, how it compares to cash accounting, and if it’s right for your business. Accruals are important because they help to ensure that a company’s financial statements accurately reflect its actual financial condition. Accrued interest refers to interest that’s been earned on an investment or a loan but hasn’t yet been paid. It would be recorded as an accrual on the company’s financial statements if the firm has a savings account that earns interest and the interest has been earned but not yet paid.
Why do I need to follow the accrual principle?
Accrual accounting ensures that all the financial statements and reports generated are GAAP-compliant. When the payment is made on Nov. 25, the consultant credits (credits decrease an asset account) the accounts receivable by $5,000 and debits (debits increase an asset account) cash with $5,000. For instance, if employees complete work in December but are paid in January, the related expense should still be recorded in December.
What Are the Principles of Accrual Accounting?

In accrual accounting, revenue and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the payment is received or made. This means that revenue is recognized when goods or services are delivered, and expenses are recognized when they are incurred, regardless of when payment is received or made. Accrual accounting is an accounting method that records revenues and expenses before payments are received or issued.
Many popular accounting software options, such as QuickBooks and Xero, offer accrual accounting as a standard feature. These programs can automatically generate and track invoices, record expenses, and reconcile bank accounts, making it easier to stay on top of your financials. Accrued revenue is recorded in the financial statements as an asset, and is recognized when the revenue is earned, not when payment is received. While the accrual method is more complex and requires more record-keeping, it is the preferred method for larger businesses and corporations. It provides a more accurate picture of a company’s financial health, making it easier to make informed decisions. This method is often favored by small businesses and sole proprietors due to its simplicity and ease of implementation.
Accrual accounting is an accounting method that recognizes revenue in the period in which it’s earned and realizable, but not necessarily when the cash is actually received. Similarly, expenses are recognized in the period in which the related revenue is recognized rather than when the related cash is paid. Cash accounting, on the other hand, records income and expenses when you receive or deliver payment for goods and services. The journal entry would involve a credit to the revenue account and a debit to the accounts receivable account for accrued revenues. This has the effect of increasing the company’s revenue and accounts receivable on its financial statements. The company would make a journal entry to record the expenses as an accrual if it has incurred expenses but has not yet paid them.
These are expenses that a company has incurred but has not yet paid within the reporting period, like wages or utilities. Expenses paid in advance, such as insurance or rent, are initially recorded as assets. These are then expensed systematically over the period to which they pertain, reflecting the consumption of the service or benefit over time. For instance, if you use the accrual-based system and sent a client an invoice in December 2022, you should have recorded the income that month. The income taxes you pay will be part of the 2022 tax year—even though you won’t receive the income itself until 2023. Most notably, the accrual method paints a better long-term picture of business trends and growth than the cash method.
Accrued expenses are accruals or expenses a company has incurred for purchasing a product/service but hasn’t paid for it yet. Prepaid expenses are accruals or expenses a company (X) pays in advance to another company (Y) before receiving the product or service from Y. The reason is simple — accrual accounting helps large corporations stay compliant, maintain transparency, and keep a true view of their financial performance. For large corporations, accrual accounting isn’t just a choice — it’s often mandatory. According to the IRS and GAAP, you’re required to use the accrual method if your business has averaged over $26 million in annual gross receipts for the past three years. This method is also mandatory if you sell products that require inventory tracking or if your business is a C corporation or a partnership with a C corporation as a partner.
This will result in overstating assets (because more has been earned) and understating liabilities/stockholders’ equity (since less is owed). They owe $50 to an employee who worked through the month of December (accrued expense). It’s beneficial to sole proprietorships and small businesses because, most likely, it won’t require added staff (and related expenses) to use. When you choose this method, you can stick with the same accounting procedures as your business grows, as it is designed to work with any size business. HighRadius propels organizations towards a 30% faster close, with Journal Entry Management significantly contributing to an accelerated month-end close by offering automated posting options. It further supports reconciliation by automating the posting of adjusted journal entries reducing manual intervention and expediting the close.


